What is the Taiga?
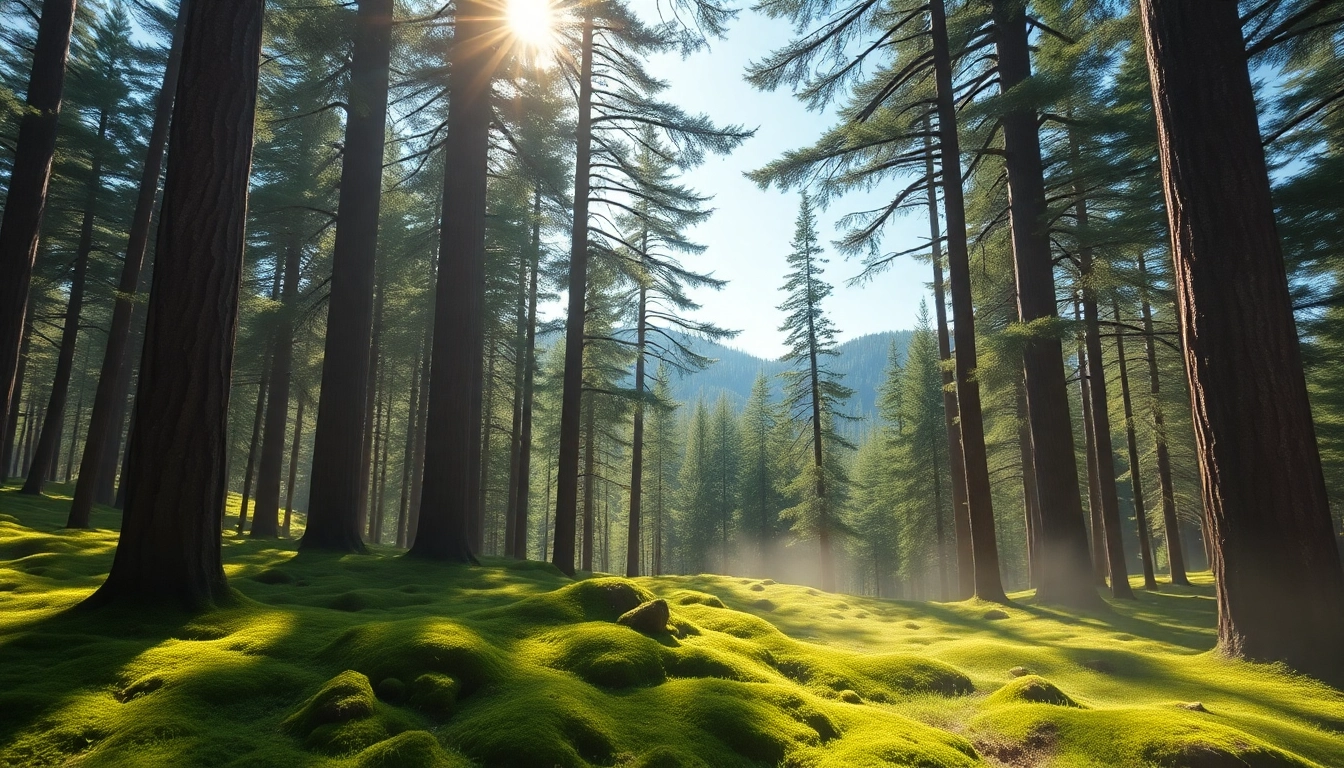
The Taiga is not just a geographical region; it is a complex biome situated across northern regions of the world, primarily characterized by its coniferous forests. It represents one of the largest and most critical ecosystems on the planet. This vast expanse of land is predominantly found in North America, Europe, and Asia, serving as a vital resource in terms of biodiversity, ecological balance, and climate regulation. One may explore various aspects, including its defining characteristics, geographical distribution, and the complex interplay of climate and weather within this unique biome. For more in-depth insights into the Taiga and its ecological significance, you can visit Taiga.
Defining Characteristics of Taiga
The Taiga, also known as the boreal forest, is characterized by specific physical and biological features that set it apart from other biomes. The most defining characteristics include:
- Vegetation: The Taiga is primarily composed of coniferous trees such as pines, spruces, and larches, which are well-adapted to the cold climates. Their needle-like leaves are designed to minimize water loss.
- Soil Composition: The soil in the Taiga is typically acidic and nutrient-poor, which can affect the types of plants that can thrive in this environment.
- Wildlife: The Taiga houses a diverse range of wildlife, including mammals like moose, wolves, and bears, as well as numerous bird species.
Geographical Distribution of Taiga
The Taiga spans across multiple continents, making it a significant component of the Earth’s ecological landscape. The geographical distribution can be defined as follows:
- North America: The Taiga extends across Alaska and parts of Canada, forming a continuous belt of forests.
- Europe: In Europe, the Taiga is prevalent in countries like Finland, Sweden, and Norway, where it merges with different types of forested areas.
- Asia: The Siberian region of Russia is primarily covered by Taiga, exemplified by its vast stretches of coniferous trees.
Climate and Weather Patterns in the Taiga
The climate of the Taiga is typically classified as subarctic, characterized by long, cold winters and short, warm summers. Understanding these weather patterns is essential for comprehending how the inhabitants of this biome adapt to their environment:
- Temperature: Average winter temperatures can drop below -25°C (-13°F), while summer temperatures can rise to 15°C (59°F).
- Precipitation: The Taiga receives moderate precipitation, mostly falling during the summer months as rain, which is crucial for the growth of vegetation.
- Seasonal Changes: Seasonal variations profoundly influence the lifecycle of flora and fauna in the Taiga, dictating growth cycles and behavioral patterns.
Flora and Fauna of the Taiga
The biodiversity of the Taiga plays a critical role in maintaining ecological stability and serves as an essential habitat for many species. The flora and fauna are well-adapted to the harsh climatic conditions, showcasing unique characteristics and behaviors.
Dominant Tree Species in the Taiga
Dominating the landscape, the Taiga is rich in several tree species that are specifically adapted to thrive in cold environments:
- Spruce: Known for their tall stature and needle-like leaves, spruces are efficient at photosynthesis even during the limited sunlight periods.
- Pine: Varieties such as the eastern white pine provide essential habitats for numerous species and play a significant role in the Taiga’s ecology.
- Larch: Unique due to their deciduous nature, larches lose their leaves in autumn, adding a distinctive touch to the evergreen landscape.
Adaptations of Animals in the Taiga
The animals residing in the Taiga exhibit remarkable adaptations that allow them to survive and thrive within this frigid ecosystem:
- Thick Fur and Fat Layer: Many mammals have developed thick fur and a layer of fat to provide insulation against the cold.
- Camouflage: Animals like the snowshoe hare adapt their fur color to blend in with seasonal changes, ensuring protection from predators.
- Behavioral Adaptations: Species such as the red fox adapt their foraging behavior, shifting their diets based on seasonal availability of food.
Unique Ecosystem Interactions in the Taiga
The Taiga hosts a variety of interactions between its flora and fauna, fostering a complex ecosystem:
- Food Webs: Various species are interlinked through intricate food webs, where each organism plays a vital role in sustaining the ecosystem.
- Symbiotic Relationships: Mutualistic relationships exist among species, such as those between certain fungi and tree roots, facilitating nutrient exchange.
- Predator-Prey Dynamics: The balance between predators and their prey shapes the populations of various species, influencing ecological resilience.
The Importance of the Taiga Ecosystem
The Taiga’s ecological significance cannot be understated. Its unique processes not only contribute to biodiversity but also play a pivotal role in global functions such as climate regulation.
Taiga and Global Climate Regulation
The Taiga is a crucial carbon sink, sequestering significant amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. This process helps mitigate climate change while highlighting the ecosystem’s importance in the global carbon cycle. The dense forests and wetland areas within the Taiga contribute to:
- Carbon Storage: Through photosynthesis, trees absorb CO2, effectively lowering greenhouse gas levels.
- Temperature Regulation: The expansive forests serve to moderate local temperatures, impacting regional climatic patterns.
Role of Taiga in Biodiversity Preservation
As one of the largest land biomes, the Taiga serves as an essential habitat for diverse species, contributing significantly to global biodiversity:
- Habitat for Endemic Species: Many species are exclusively found in Taiga, highlighting its critical role in species conservation.
- Genetic Diversity: The various plant and animal species contribute to genetic diversity, which is crucial for resilience against diseases and environmental changes.
Taiga’s Influence on Human Culture and Economy
The Taiga has intertwined with human history and culture, offering resources and influencing livelihoods:
- Resource Provision: The forests are a source of timber, food, and medicinal plants, significantly impacting local economies.
- Cultural Significance: Many indigenous communities regard the Taiga as sacred, integrating its elements into cultural practices and traditions.
Threats Facing the Taiga
Despite its ecological importance, the Taiga faces significant threats that jeopardize its integrity and sustainability. Understanding these threats is crucial for conservation efforts.
Impact of Climate Change on the Taiga
Climate change poses a significant threat to the Taiga, affecting its delicate balance:
- Temperature Increases: Rising temperatures lead to shifts in species distributions, potentially threatening local biodiversity.
- Altered Precipitation Patterns: Changes in precipitation can affect water availability for plants and animals, disrupting entire ecosystems.
Logging and Deforestation in the Taiga
Logging activities have emerged as a major threat, leading to habitat loss and disruption:
- Unsustainable Practices: Intensive logging can lead to forest fragmentation, impacting wildlife habitats.
- Impact on Carbon Sequestration: Deforestation reduces the forest’s ability to sequester carbon, further exacerbating climate change.
Conservation Efforts for the Taiga
Recognizing the challenges, various conservation efforts are underway aimed at protecting the Taiga:
- Protected Areas: Establishing protected areas within the Taiga helps preserve critical habitats and species.
- Sustainable Resource Management: Implementing sustainable practices ensures that resource extraction doesn’t compromise the integrity of the ecosystem.
Visiting the Taiga
For those interested in exploring the Taiga, numerous opportunities exist to experience its unique beauty and biodiversity. Sustainable interactions can enhance appreciation for this valuable ecosystem while promoting conservation.
Best Locations to Experience the Taiga
Several locations offer breathtaking views and immersive experiences in the Taiga:
- The Canadian Boreal Forest: Home to expansive forested areas teeming with wildlife, making it an ideal spot for hiking and camping.
- Siberia: Known for its dramatic scenery and diverse ecosystems, Siberia showcases the Taiga’s vastness.
- Scandinavia: The Taiga here, rich in natural beauty, provides numerous national parks and reserves for visitors.
Activities to Enjoy in the Taiga
Visitors can engage in various activities that enhance their appreciation of the Taiga:
- Wildlife Watching: Observing unique species in their natural habitat can offer educational and enriching experiences.
- Hiking and Camping: Explore the diverse landscapes through hiking trails, allowing for immersive nature experiences.
- Photography: Capture the stunning vistas and unique wildlife that thrive within the Taiga.
How to Support Taiga Conservation while Visiting
Visitors can play a role in preserving the Taiga while enjoying its beauty:
- Choose Eco-friendly Tours: Opt for guided tours that prioritize sustainability and conservation.
- Leave No Trace: Practice responsible camping and hiking by minimizing environmental impact.
- Educate Yourself and Others: Share knowledge about the importance of the Taiga and the threats it faces to raise awareness.